The Problem:
A cyclist riding at 5 m s1 starts to accelerate, and 200 metres later she is riding at 7 m s’. Find her acceleration, assumed constant.
Douglas Quadling Mechanics1 Exercise1C Q4
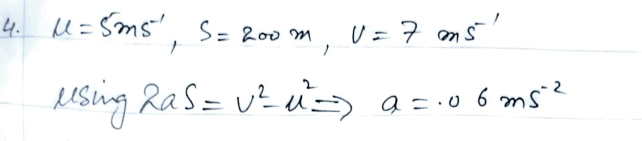
Problem: A cyclist is riding at 5 m/s and starts to accelerate. After traveling 200 meters, she is riding at 7 m/s. Assuming constant acceleration, find her acceleration.
Solution:
Step 1: Understand the Problem
We are given:
- Initial speed (u) = 5 m/s.
- Final speed (v) = 7 m/s.
- Distance (s) = 200 meters.
- Acceleration (a) = constant (unknown).
We need to find:
- The acceleration (a) of the cyclist.
Step 2: Use the Equation of Motion
Since the cyclist has constant acceleration, we use the equation:
v² = u² + 2as
Where:
- v = final speed,
- u = initial speed,
- a = acceleration,
- s = distance.
Step 3: Substitute the Known Values
Substitute the known values into the equation:
v² = u² + 2as
7² = 5² + 2 * a * 200
49 = 25 + 400a
Step 4: Solve for Acceleration (a)
Subtract 25 from both sides:
49 – 25 = 400a
24 = 400a
Divide both sides by 400:
a = 24 / 400
a = 0.06 m/s²
Final Answer:
The cyclist’s acceleration is 0.06 m/s².
Summary:
- The cyclist’s acceleration is 0.06 m/s².