The Problem:
A police car accelerates from 15 m/s to 35 m/s in 5 seconds. The acceleration is constant. Illustrate this with a velocity-time graph. Use the equation v=u+ at to calculate the acceleration. Find also the distance travelled by the car in that time.
Douglas Quadling Mechanics 1
Exercise 1B Q1
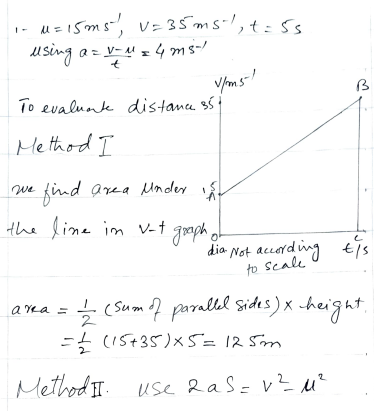
A police car accelerates from 15 m/s to 35 m/s in 5 seconds. The acceleration is constant. Illustrate this with a velocity-time graph. Use the equation v = u + at to calculate the acceleration. Find also the distance traveled by the car in that time.
Solution:
Step 1: Calculate the Acceleration
Using the equation:
v = u + at
Rearrange to solve for a:
a = (v - u) / t
Substitute the known values:
a = (35 - 15) / 5
a = 4 m/s²
Step 2: Calculate the Distance Traveled
Using the equation:
s = ut + (1/2) a t²
Substitute the known values:
s = (15)(5) + (1/2)(4)(5)²
s = 75 + 50
s = 125 m
Step 3: Velocity-Time Graph
The velocity-time graph is a straight line starting at (0, 15) and ending at (5, 35). The slope of the line represents the acceleration (a = 4 m/s²).
Final Answer:
- Acceleration (a): 4 m/s²
- Distance traveled (s): 125 m
- Velocity-Time Graph: A straight line starting at
(0, 15)and ending at(5, 35).