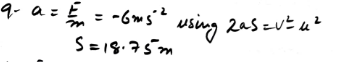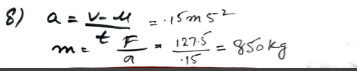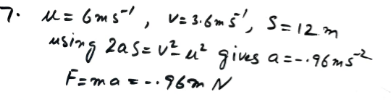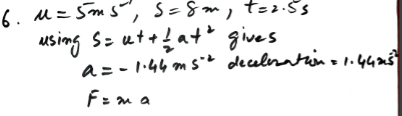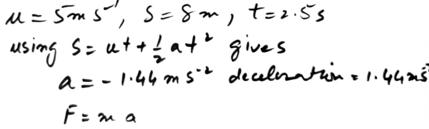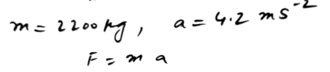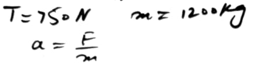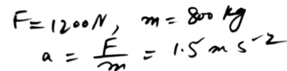A hockey player hits a stationary ball, of mass 0.2 kg. The contact time between the stick and the ball is 0.15s and the force exerted on the ball by the stick is 60 N. Find the speed with which the ball leaves the stick.
A hockey player hits a stationary ball, of mass 0.2 kg. The contact time between the stick and the ball is 0.15s and the force exerted on the ball by the stick is 60 N. Find the speed with which the ball leaves the stick.