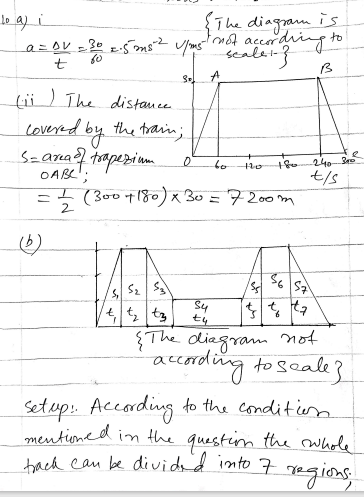
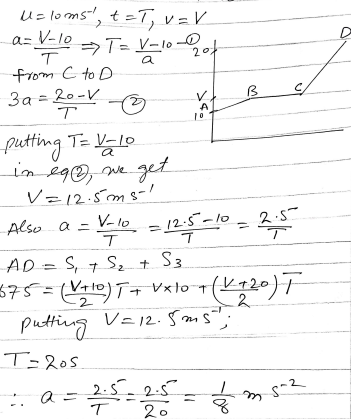
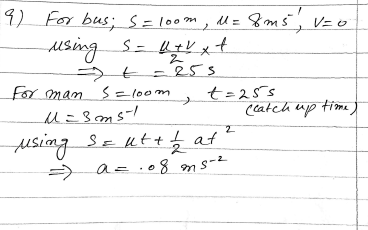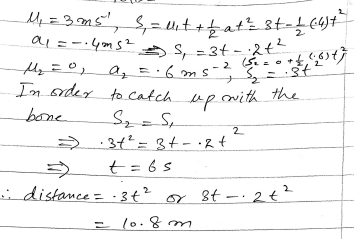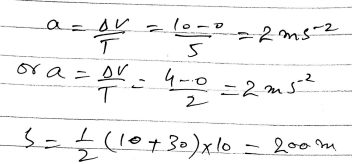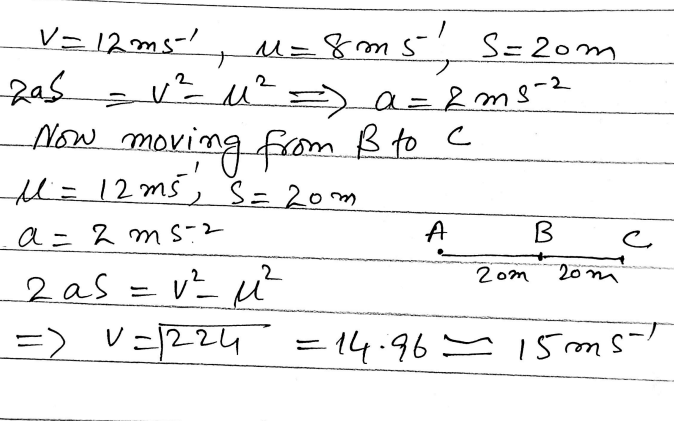A cyclist is free-wheeling down a long straight hill. The times between passing successive kilometre posts are 100 seconds and 80 seconds. Assuming his acceleration is constant, find this acceleration.
A cyclist is free-wheeling down a long straight hill. The times between passing successive kilometre posts are 100 seconds and 80 seconds.