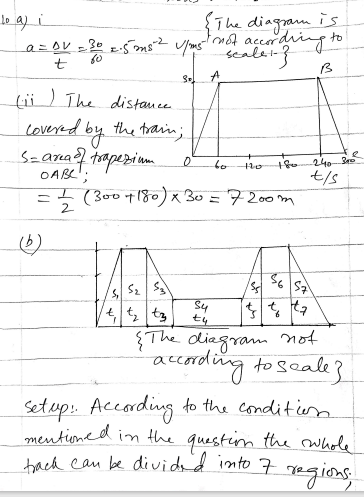
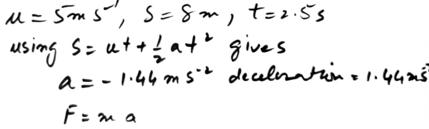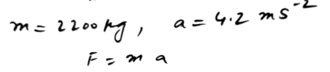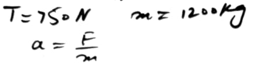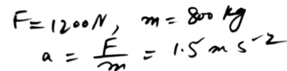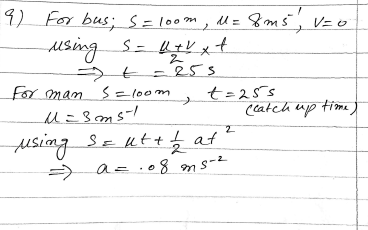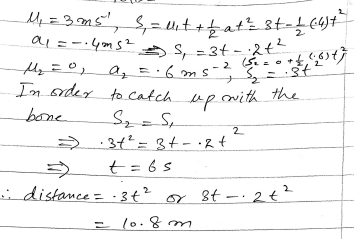A wooden block of mass m kg is at rest on a table, 1.6 metres from an edge. The block is pulled directly towards the edge by a horizontal string. The tension in the string has magnitude 0.2m N. Calculate the time taken for the block to reach the edge of the table.
A wooden block of mass m kg is at rest on a table, 1.6 metres from an edge. The block is pulled directly towards the edge by a horizontal string.