A particle of mass 5 kg is pulled, with constant speed, along a rough surface by a horizontal force of magnitude 45 N. …..
Title: Analysis of Forces on a Moving Particle
Scope: In this scenario, a particle of mass 5 kg is being pulled along a rough surface with a constant speed by a horizontal force. The objective is to calculate the magnitude of the frictional force when the particle is pulled with a force of 45 N, and subsequently, to determine the acceleration of the particle when the force is increased to 55 N. The analysis involves the consideration of the gravitational force, frictional force, and Newton’s second law.
A particle of mass 5 kg is pulled, with constant speed, along a rough surface by a horizontal force of magnitude 45 N. ……
Analysis:
A particle of mass 5 kg is pulled, with constant speed, along a rough surface by a horizontal force of magnitude 45 N. …….
1. Calculation of Frictional Force: The frictional force (�frictionFfriction) acting on the particle is determined by the equation: �friction=�⋅�⋅�Ffriction=μ⋅m⋅g where �μ is the coefficient of friction, �m is the mass of the particle (5 kg), and �g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s²).
2. Determination of Acceleration with Increased Force: When the horizontal force is increased to 55 N, and the particle continues to move with constant speed, the net force remains zero. The frictional force needs to be recalculated using the new force (�applied=55 NFapplied=55 N), and the acceleration (�a) can be found using Newton’s second law: Σ�=�⋅�ΣF=m⋅a
A particle of mass 5 kg is pulled, with constant speed, along a rough surface by a horizontal force of magnitude 45 N. …….
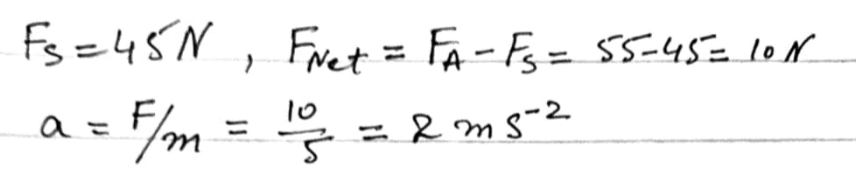
Conclusion: The analysis provides insight into the forces acting on the particle. By first calculating the frictional force at an initial force of 45 N and then determining the acceleration when the force is increased to 55 N, a comprehensive understanding of the dynamic equilibrium of forces on the moving particle is achieved. The specific numerical values can be obtained with the knowledge of the coefficient of friction (�μ), which is not provided in the given information.
