#1 Title: Pre-Flight Dynamics: Unveiling the Force of Aircraft Acceleration; For the first stage of its motion on the runway, before take-off, an aircraft of mass 2200 kg has a constant acceleration of 4.2 m s2……
In the prelude to soaring skies, an aircraft of substantial mass, weighing in at 2200 kg, navigates the runway with an initial stage of constant acceleration. This acceleration, a formidable 4.2 m/s, sets the stage for the aircraft’s ascent. The crux of this numerical journey lies in calculating the force required to usher in and sustain this acceleration, an essential parameter in the orchestration of a successful take-off.
Douglas Quadling Mechanics1 Exercise 2A Q3
For the first stage of its motion on the runway, before take-off, an aircraft of mass 2200 kg has a constant acceleration of 4.2 m s2…………
Solution
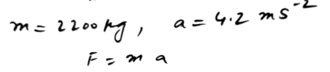
#2 Scope without Calculation: Forces at Play in Aircraft Acceleration
1. Introduction:
For the first stage of its motion on the runway, before take-off, an aircraft of mass 2200 kg has a constant acceleration of 4.2 m s2….
- The scenario involves an aircraft with a mass of 2200 kg undergoing a constant acceleration of 4.2 m/s2 during the initial stage of its motion on the runway.
2. Scenario Description:
- The aircraft’s acceleration is the focal point, prompting an exploration into the force necessary to facilitate and maintain this acceleration, a critical phase before take-off.
3. Objectives:
- The primary goal is to calculate the force required for the aircraft’s acceleration, an integral factor in the aviation dynamics during the initial runway phase.
4. Significance:
- Unraveling the force of acceleration provides insights into the propulsive requirements for an aircraft’s successful take-off, influencing design considerations and operational strategies.
5. Exploration Focus:
- The numerical inquiry centers on dissecting the relationship between mass, acceleration, and force, offering a glimpse into the forces propelling aircraft during the early stages of flight.
6. Newtonian Mechanics:
- The exploration draws on fundamental principles of Newtonian mechanics, particularly the force-mass-acceleration relationship, to model the aircraft’s motion.
7. Aviation Dynamics:
- The scenario involves complexities related to the dynamics of aviation, necessitating an analysis of forces and their impact on the aircraft’s initial acceleration.
8. Practical Application:
- Findings contribute to the practical understanding of forces at play in aviation, providing real-world implications for optimizing take-off procedures and aircraft performance.
Conclusion:
For the first stage of its motion on the runway, before take-off, an aircraft of mass 2200 kg has a constant acceleration of 4.2 m s2…
- The numerical investigation promises to unveil the force required for the aircraft’s initial acceleration, offering valuable insights into the dynamic forces shaping the early phases of flight on the runway.
The Next Question:https://alevelmechanics1.com/692/a-water-skier-is-being-towed-by-a-motor-boat-given-that-her-acceleration-of-0-8-m-s-is-provided-by-a-force-of-52-n-
