The Problem:
A train travelling at 20 m /s starts to accelerate with constant acceleration. It covers the next kilometre in 25 seconds. Use the equation s = ut+1/2at^2 to calculate the acceleration. Find also how fast the train is moving at the end of this time. Illustrate the motion of the train with a velocity-time graph. How long does the train take to cover the first half kilometre?
Douglas Quadling Mechanics 1
Exercise 1B Q3
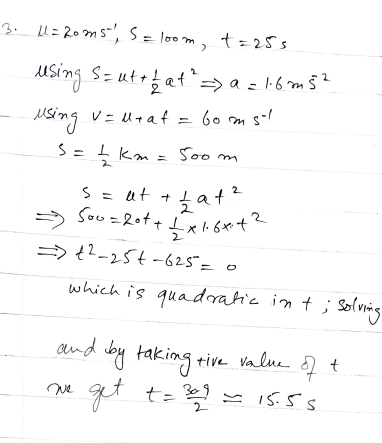
Problem Statement
A train traveling at 20 m/s starts to accelerate with constant acceleration. It covers the next kilometer in 25 seconds. Use the equation s = ut + 0.5 * a * t^2 to calculate the acceleration. Find also how fast the train is moving at the end of this time. How long does the train take to cover the first half kilometer?
Solution
1. Calculate Acceleration
Using the equation: s = ut + 0.5 * a * t^2
Given:
- Initial velocity (u) = 20 m/s
- Distance (s) = 1000 meters
- Time (t) = 25 seconds
Plugging in the values:
1000 = 20 * 25 + 0.5 * a * (25)^2 1000 = 500 + 0.5 * a * 625 1000 - 500 = 312.5 * a 500 = 312.5 * a a = 500 / 312.5 a = 1.6 m/s²
Acceleration (a) = 1.6 m/s²
2. Calculate Final Velocity
Using the equation: v = u + a * t
Plugging in the values:
v = 20 + 1.6 * 25 v = 20 + 40 v = 60 m/s
Final Velocity (v) = 60 m/s
3. Time to Cover the First Half Kilometer
Using the equation: s = ut + 0.5 * a * t^2
Given:
- Distance (s) = 500 meters
Plugging in the values:
500 = 20 * t + 0.5 * 1.6 * t^2 500 = 20t + 0.8t^2 0.8t^2 + 20t - 500 = 0
Solving the quadratic equation:
t = [-20 ± sqrt(20^2 - 4 * 0.8 * (-500))] / (2 * 0.8) t = [-20 ± sqrt(400 + 1600)] / 1.6 t = [-20 ± sqrt(2000)] / 1.6 t = [-20 ± 44.72] / 1.6
Taking the positive root:
t = (24.72) / 1.6 t = 15.45 seconds
Time to cover the first half kilometer = 15.45 seconds