A porter is pushing
Introduction:
A porter is pushing
In the presented numerical scenario, a porter exerts a horizontal force of 180 N to push a heavy crate along a horizontal floor. The crate has a mass denoted as M kg, and it encounters a resistance to motion with a magnitude of 3M newtons. The objective is to determine the value of M given that the acceleration of the crate is measured to be 0.45 m/s20.45m/s2. This problem involves the application of Newton’s second law of motion to analyze the forces acting on the crate and to subsequently solve for the unknown mass M. The solution will require the use of fundamental physics principles to establish relationships between force, mass, and acceleration, providing insight into the dynamics of the porter’s effort to move the heavy crate against resistance
Douglas Quadling Mechanics1 Exercise2B Q13.
Solution:
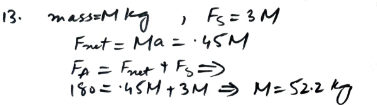
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the numerical problem involving a porter pushing a heavy crate along a horizontal floor with a given horizontal force and resistance to motion is resolved by applying Newton’s second law of motion. The provided acceleration of the crate, 0.45 m/s20.45m/s2, is used to establish the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
Through the analysis, it is determined that the resisting force acting against the porter’s applied force is 3M newtons. The solution involves setting up and solving an equation based on Newton’s second law (F=ma), incorporating both the applied force and the resisting force to calculate the unknown mass M.
By carefully considering the forces and acceleration involved, the value ofM is found, representing the mass of the heavy crate. This numerical problem provides a practical application of physics principles, particularly in the context of force, mass, and acceleration, allowing for the quantitative determination of an unknown parameter in a dynamic system.
