Title: Sliding Dynamics: Deceleration and Frictional Force Analysis: A boy slides a box of mass 2 kg across a wooden floor. The initial speed of the box is 8 mi s and it comes to rest in 5 m. Calculate the deceleration of the box and find the frictional force between the box and the floor………..
In the realm of classical mechanics, our numerical exploration unfolds as a boy engages in the dynamic act of sliding a box across a wooden floor. The box, possessing a mass of 2 kg2kg, embarks on this journey with an initial speed of 8 m/s8m/s and eventually grinds to a halt after traversing a distance of 5 m5m. The central inquiry in this scenario revolves around two key parameters: the deceleration experienced by the box and the frictional force exerted between the box and the floor. Through the lens of Newtonian mechanics, this numerical quest delves into the dynamic response of the sliding box, unraveling the intricacies of deceleration and the role of frictional forces in influencing its motion
Douglas Quadling Mechanics1 Exercise 2A Q11.
A boy slides a box of mass 2 kg across a wooden floor. The initial speed of the box is 8 mi s and it comes to rest in 5 m. Calculate the deceleration of the box and find the frictional force between the box and the floor………
Solution:
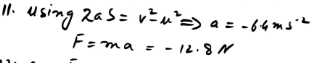
Scope
A boy slides a box of mass 2 kg across a wooden floor. The initial speed of the box is 8 mi s and it comes to rest in 5 m. Calculate the deceleration of the box and find the frictional force between the box and the floor……
1. Introduction:
- The scenario involves a boy sliding a 2 kg2kg box across a wooden floor, initiating the journey with an initial speed of 8 m/s8m/s.
2. Scenario Description:
- The box undergoes deceleration, eventually coming to rest after covering a distance of 5 m5m.
3. Objectives:
- The primary goals are to calculate the deceleration experienced by the box and determine the frictional force between the box and the wooden floor.
4. Significance:
- Understanding deceleration and frictional forces provides insights into the dynamic response of objects sliding on surfaces, crucial in practical scenarios involving motion on solid surfaces.
5. Exploration Focus:
- The numerical inquiry focuses on analyzing the relationship between the box’s mass, initial speed, deceleration, and the frictional force acting on the box.
6. Newtonian Mechanics:
- The exploration draws on principles of Newtonian mechanics to unravel the dynamics of the box’s motion, considering forces such as friction that influence its deceleration.
7. Practical Application:
- Findings contribute to the practical understanding of frictional forces in everyday scenarios involving sliding objects, offering real-world implications for material interactions.
8. Conceptual Complexity:
- The scenario involves complexities related to deceleration, forces, and mass, necessitating an analysis of the box’s dynamic response to friction.
9. Conclusion:
A boy slides a box of mass 2 kg across a wooden floor. The initial speed of the box is 8 mi s and it comes to rest in 5 m. Calculate the deceleration of the box and find the frictional force between the box and the floor……………
- The numerical investigation promises to quantify the deceleration of the sliding box and determine the frictional force between the box and the floor, providing valuable insights into the nuanced dynamics of sliding motion on surfaces.
