Title: Friction on Ice: Analyzing Deceleration and Resistive Forces Two children are sliding a box to each other on a frozen lake…..
In the winter spectacle of frozen lakes, a numerical scenario unfolds as two children engage in the playful act of sliding a box between them. The box, with a mass of 0.4 kg, embarks on a frosty journey, departing from one child with an initial speed of 5 m/s. The box glides across the ice, covering a distance of 8 m to reach the awaiting second child in a span of 2.5 s. This captivating scenario prompts a dual inquiry: first, to calculate the deceleration experienced by the sliding box, and second, to determine the frictional force that steadfastly resists its motion across the icy surface. Through the application of Newtonian mechanics and principles of friction, this numerical exploration delves into the chilly dynamics of the box’s motion, unraveling the intricacies of deceleration and the resistive forces at play on the frost-kissed lake.
Douglas Quadling Mechanics1 Exercise 2A Q6
Two children are sliding a box to each other on a frozen lake…….
Solution:
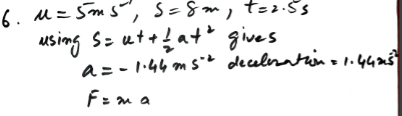
1. Introduction:
Two children are sliding a box to each other on a frozen lake……..
- The scenario involves a particle (P) of mass mkg moving with constant deceleration along a straight line, passing through points A and B.
2. Scenario Description:
- Particle P exhibits speeds of 6 m/s6m/s at point A and 3.6 m/s3.6m/s at point B.
- The known distance between points A and B is 12 m12m.
3. Objectives:
- The primary goal is to calculate, in terms of the particle’s mass (m), the magnitude of the force resisting the motion of particle P.
4. Significance:
- Understanding the resisting force provides insights into the factors influencing the deceleration of particle P, shedding light on its motion dynamics.
5. Exploration Focus:
- The numerical inquiry centers on analyzing the relationship between deceleration, mass, and the resulting force, unraveling the forces at play during the particle’s motion.
6. Newtonian Principles:
- The exploration draws on fundamental principles of Newtonian mechanics, particularly those related to deceleration, to model the motion of particle P.
7. Kinematics:
- The scenario involves complexities related to the kinematics of deceleration, necessitating an analysis of speed changes and resulting forces.
8. Practical Application:
- Findings contribute to the practical understanding of forces influencing particle motion, providing real-world implications for dynamic scenarios involving deceleration.
Conclusion:
Two children are sliding a box to each other on a frozen lake………
- The numerical investigation promises to express, in terms of the particle’s mass (m), the magnitude of the force resisting the motion of particle P, offering valuable insights into the dynamics of deceleration in particle motion.
